Difference Between MP3 and MP4: Which is Better For Everyday life?

As the naming says, we might think that MP4 should be just next MP3, but despite their names these formats are from different classes. MP3 is an audio format and an encoding format and its formal name is MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, so it’s a part of an MP2 container. On the other hand, MP4 is a modern media container format that can store both video and audio streams.
It’ll be more correct to compare MP2 with MP4 as they are both container formats with specifications, developed by the MPEG workgroup in the US. But we’ll be focusing on audio in this article, so let’s compare MP3 with audio codecs that are used in MP4. For example, AAC.
MP3 is the most popular lossy audio format which applies digital compression to waveform. The compression algorithm simplifies audio at non-hearable ranges, higher than 20,000 Hz in frequency and after high-level peaks and spikes in time. In other words, it takes into account sound perception by a human ear, also called psychoacoustics.
MP3: Application, Definition, History, Device Adaptation
MP3 is a lossy encoding standard for digital audio. Also, .mp3 is a file format and extension for audio files compressed with an MP3 algorithm. MP3 compression reduces the accuracy of sound signals and its components beyond the hearing capabilities of most humans. For example, an average adult can’t hear frequencies above 18 000 Hz and below 40 Hz.
Also, there are psychoacoustic parameters taken into consideration. For example, when an audio track hits a peak volume level, like a drum hit, the human ear can’t recognize subtle audio detail a few milliseconds afterwards and it’s also removed during the MP3 compression.
Lossy MP3 audio encoding helps you find balance between the file size and the audio quality. Both network bandwidth and MP3 quality parameter is a bitrate. In MP3, bitrate specifies how many bits of audio data are reproduced in a certain amount of time.
MP4: Application, Definition, History, Device Adaptation
Its full name is MPEG-4 Part 14 and it’s a digital multimedia container format. It can store multiple video and audio tracks, subtitles, and thumbnails like in DVD menus. It has been designed for playing back over the Internet so it flawlessly supports streaming and it’s used and accepted by most video sharing services, like YouTube.
MP4 format was created in 2001 based on Apple's QuickTime and MPEG-4 Part 12. It has a similar, yet extended set of features than its counterpart, QT. MP4 supports a variety of codecs for video streams, such as H.264 or AVC. It can be played by most video player apps and devices, such as smartphones, tablets and computers.
MP4 has extended audio compatibility too. It supports many codecs, channels from mono to Dolby Digital 5:1 as well as other sound parameters. It can store up to 16 tracks of audio tracks (e.g., for switching languages while watching the movie).
When it comes to web, it’s also widely used. It’s MIME type is video/mp4 and it’s supported by all modern web browsers. If an MP4 container contains audio tracks only, it’s usually has an .m4a extension.
MP4 Audio Codec support
MP4 is a very versatile media container format and it supports various audio codecs:
-
AAC
-
AC3
-
Apple Lossless (M4A)
-
MP1
-
MP2
-
MP3
-
ALS
-
SLS
-
CELP
-
HVXC
-
TwinVQ
-
TTSI
-
SAOL
For the vast majority of cases, AAC is used within an MP4 container as a more efficient audio codec. AC3 and MP3 are used less frequently.
Visual comparison MP3 vs MP4
To provide a visual comparison of two formats and their specifications, we’ll use a free tool Audacity with an installed LAME MP3 codec (version 3.1). We’ll record a voiceover and save the file both as MP3 and as MP4/AAC.
MP3 graphical snapshot
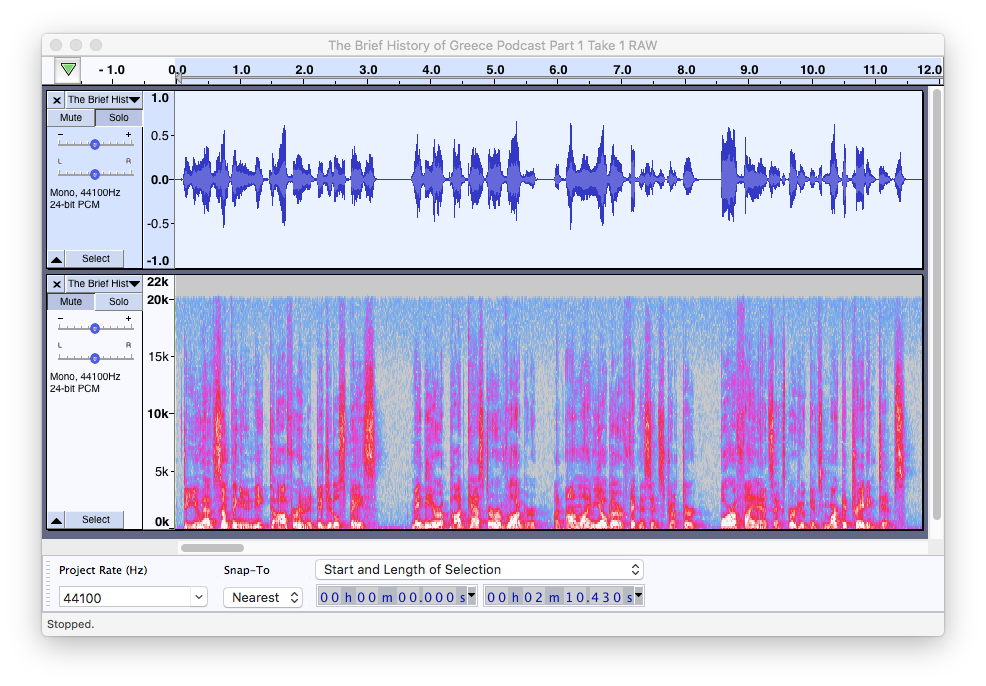
As you can see, all frequencies above 20,000 Hz don’t exist because they were cut out during compression. There is much more than that operation in MP3 compression, but this is the most obvious. If we zoom in, we’ll see more differences in the spectral view between MP4 and MP3, yet most of these differences don’t affect the sound quality.
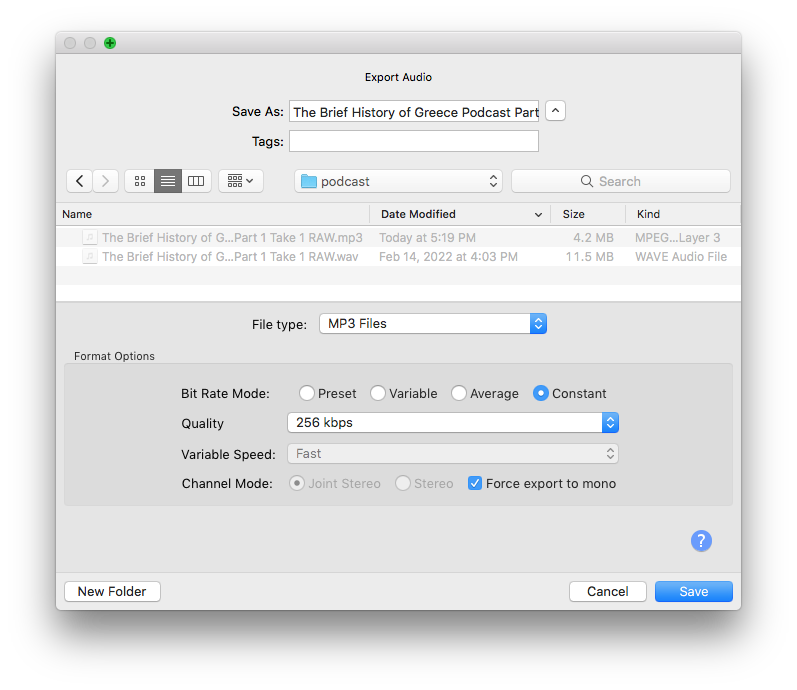
MP3 save settings
There are few parameters of compression that you can choose while exporting or saving MP3 files. The one that’s the most important is a bitrate
It can be constant or a variable depending on the density of information in audio. Music is filled with information so it’s better to use Constant bitrate. Dialogues and voiceovers have silence between phrases and using a Variable bitrate might help you save some space. Anyway, constant bitrate will potentially cause fewer artifacts.
Quality parameters range from 128 to 320 kbps. We recommend setting it at 256 kbps for dialogues and 320 — for music.
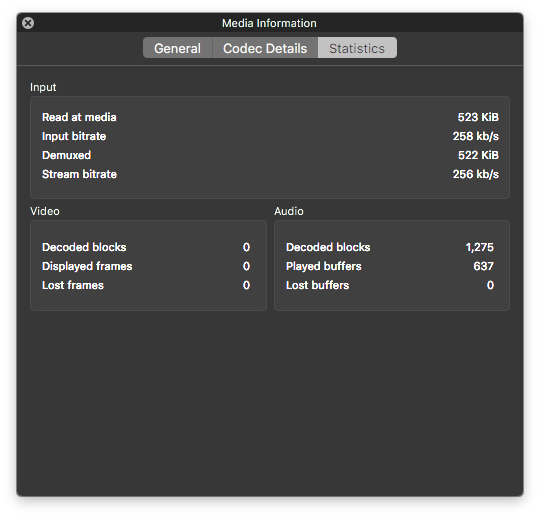
MP3 bitrate information
Now, let’s check the amount of information that a MP3 streams each second. It’s 256 kbps.
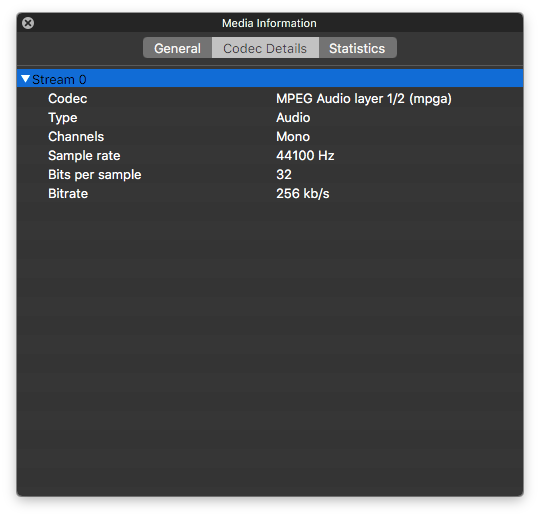
MP3 codec information
The codec used is MPEG Audio Layer 1/2 (mpga). The sample rate is the same, which is 44,100 Hz. Is a CD quality standard and it works for most devices, programs and online services.
Convert source file to MP4
-
Go to https://online-audio-converter.com and upload your source .wav file of your original recording if you have it. Try to avoid uploading an .mp3 file because it already has compression applied.
-
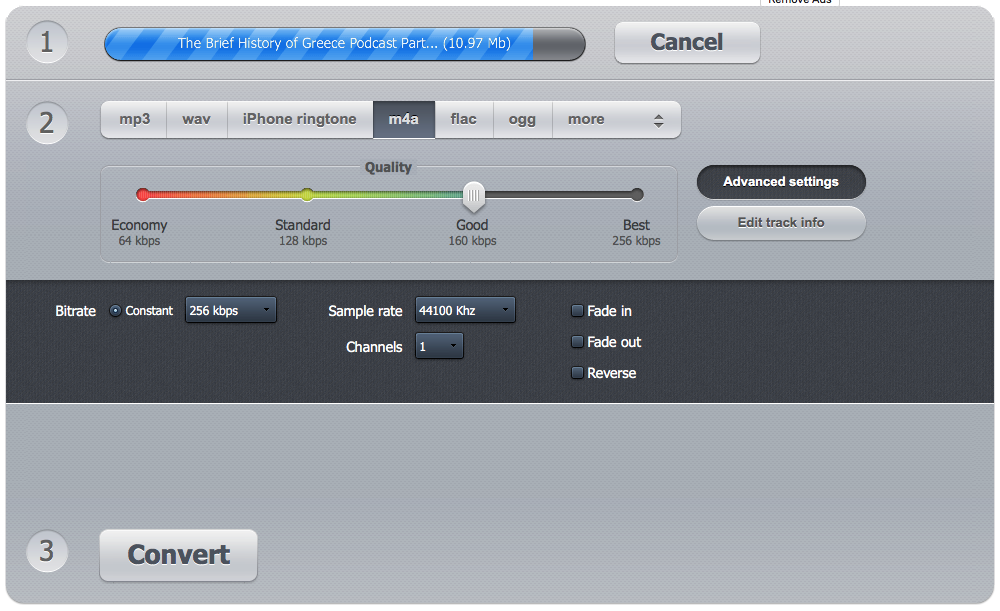
When your .wav is uploaded, select m4a as the destination. It’s an MP4 container with just audio. By default, the Advanced Audio Codec (AAC) is used.
-
Open Advanced Settings. M4A/AAC is more efficient than MP3, so we can keep the bitrate one step lower, and it’ll give a comparable audio result with a smaller file size. However, I’ll use the same 256 kbps and one channel (mono) to estimate the difference.
MP4 graphical snapshot
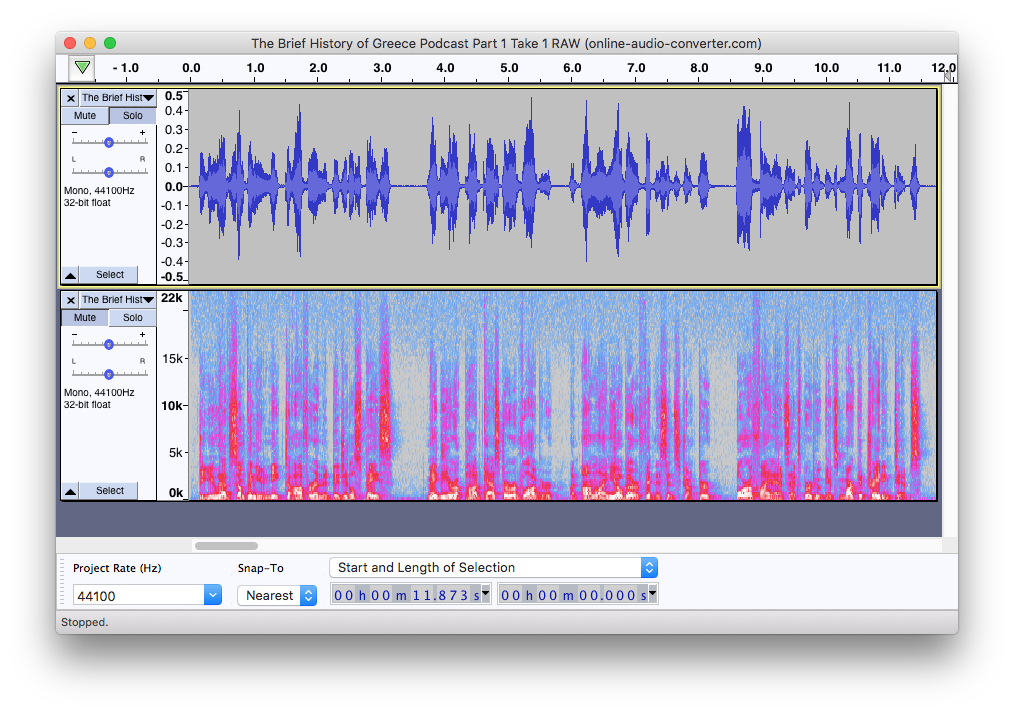
Unlike MP3 spectrograms, the MP4/AAC codec doesn’t cut off the white noise in higher frequencies. The compression can hardly be seen.
MP4 bitrate information
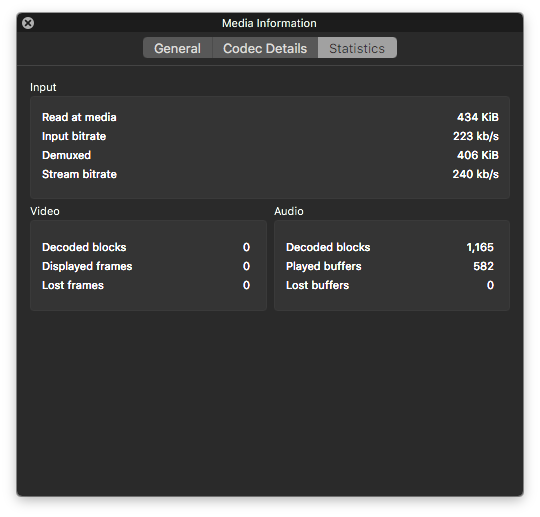
Now, let’s check the amount of information that MP4/AAC audio conveys. It’s 240 kbps, a little less than the 256 kbps that we set. It means that the data is compressed better without losing any data (like ZIP archives).
MP4 codec information
The codec used is MPEG AAC Audio. The sample rate is the same, which is 44,100 Hz. Is a CD quality standard and it works for most devices, programs and online streaming services.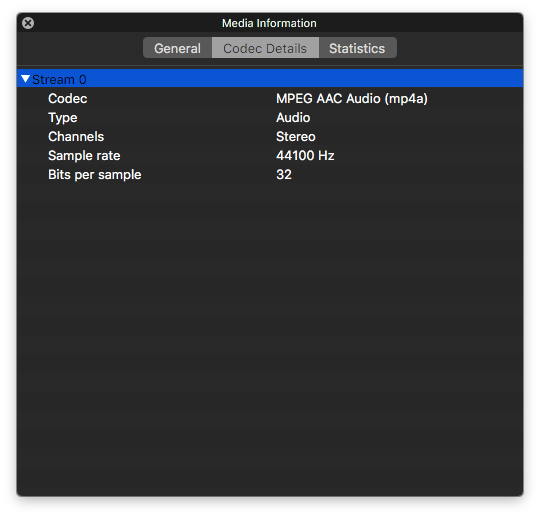
Is MP4 quality better than in MP3?
The quality is definitely better in the MP4 version than in the MP3 because it uses a more advanced audio codec. Being originated from the same lossless WAV source file, the MP4/AAC file size is almost 50% less than MP3 with comparable quality settings. The spectrogram shows less obvious artifacts on the MP4 file as well.
The hearing test is subjective and there is no difference in a spoken track in both MP3 and MP4 formats because the quality was high.
Last but not least, MP4/AAC is more economical when it comes to building a huge online service. All music streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music use AAC codec (or its analogs) in favor of older MP3. It helps them immensely in cutting cloud storage costs and also they can deliver content to millions of users faster.
Do I lose sound quality if I convert MP3 to a MP4 format?
It all depends on the quality of the source MP3. If it’s 320 kbps and you are saving it to 128 kbps MP4 audiotrack, of course there’ll be a loss of quality.
If you set MP3 quality to lower bitrates (apply heavier data compression), like 128 kbps and less, digital artifacts may become noticeable and even distracting. The good recommendation is to pre-listen your MP3 audio using reference headphones or studio monitors.
What is Better for YouTube MP3 or MP4?
YouTube is a video service so you can’t upload audio-only files, they have to be converted to video files beforehand, like MP4. The container can have any audio stream, including MP3 and M4A/AAC. As a little trick, you can put a static image and add a soundtrack of your podcast and convert everything using our service.
YouTube Music service that is a part of YouTube, supports audio files without video. As mentioned on the YouTube help pages, you can upload MP3, M4A, FLAC and other formats.
There’s no clear reply on what format is better to upload. It doesn’t matter much. What matters is that you make sure that you attach an audio track in the highest possible Quality. YouTube will create versions of audio files with a reduced sound quality to keep up with slower bandwidth for some viewers.