In this article we will discuss audio encoding settings that affect the quality of sound. Understanding the conversion settings can help you select the optimal sound encoding properties in terms of file size relative to sound quality.
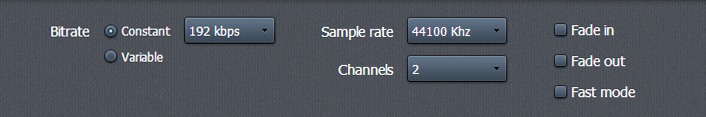
What is bitrate?
Bitrate is the amount of data consumed to transmit audio stream per unit of time. For example, bitrate of 128 kbps stands for 128 kilobit per second and means that one second of sound is coded with 128 thousand bit (1 byte = 8 bit). If you convert this into kilobytes, one second of sound takes around 16 KB.
Thus, the higher the bitrate of a track, the more space on your computer it is going to take. However, within the same format, the higher bitrate allows recording the better quality sound. For example, if you convert CD audio into MP3 the bitrate of 256 kbps will give a much better sound quality than the 64 kbps bitrate.
Because the hard drive space nowadays is relatively cheap, we recommend converting into MP3 with the bitrate of at least 192 kbps or higher.
Bitrate can also be classified as constant or variable.
The Difference between Constant (CBR) and Variable (VBR) bitrate
The constant bitrate means the coding of each sound segment consumes constant amount of bit. However, the sound structure can be different, and coding a silent segment requires much less bit than coding an intense sound segment. Unlike the constant bitrate, the variable bitrate automatically adjusts the quality of coding at various intervals. Thus, the intervals that are simple in terms of coding will use lower bitrate, while the more complex intervals will be coded with the higher bitrate. The use of variable bitrate allows achieving higher quality of sound while keeping the file size down.
What is sampling rate?
This term is used in converting analog signal into digital form and defines the number of samples (sample measurements of signal level) per second required to convert a signal.